
Imagine a new kind of internet where all the content you read is more customized to you than ever and truly understands everything you say, whether it be through text, voice, or other media.
The web is about to enter a new stage of its evolution. Innovators have called it Web 3.0
There may be a few early-stage Web 3.0 applications presently available, but their full potential cannot be utilized until the new internet is fully integrated into the web infrastructure.
What is the Web?

The World Wide Web also called the Web or WWW, is an information system that makes it possible to access papers and other web resources through the Internet.
Programs like web browsers can access documents and other downloaded media made available to the network through web servers.
What are Different Types Of The Web?
There are mainly 3 types of the web,
- Web1.0
- Web2.0
- Web3.0
What is the Web 3.0?

The third generation of web technologies is known as Web 3.0 (Web3). The WWW serves as the basic layer of the internet, offering website and application services.
Through technologies like machine learning (ML), big data, decentralized ledger technology (DLT), etc.
websites and apps will be able to handle information in a smart, human-like manner in WEB3.0.
Tim Berners-Lee, the creator of the World Wide Web, first referred to Web 3.0 as the Semantic Web.
Its goal was to create a more independent, intelligent, and open internet.
Users and machines will be able to communicate with data as well.
Programs must be capable of understanding information theoretically and culturally for this to happen, though.
With this in mind, the semantic web and artificial intelligence are the two pillars of Web 3.0.
The evolution of Web 3.0 technologies
Web 3.0 will develop as a natural evolution of current web tools mixed with cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence, as well as from consumer connectivity and growing internet usage.
Internet 3.0 appears to be an advance above web 1.0 and 2.0.
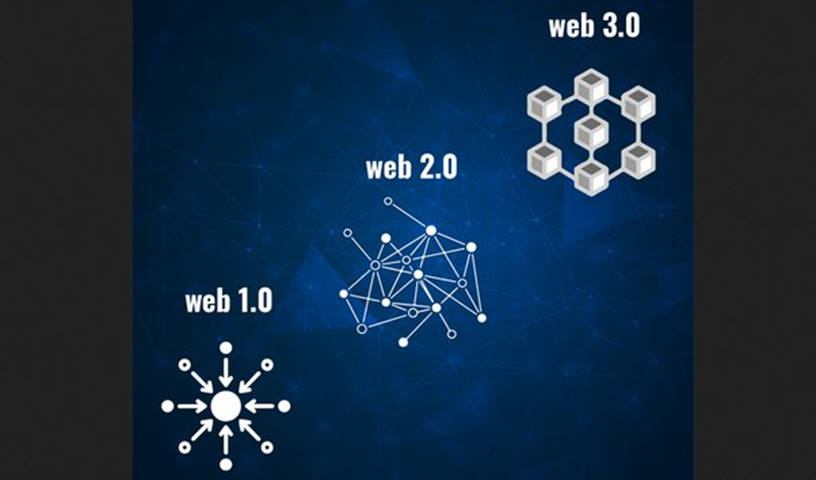
Web 1.0 (1989-2005)
While just providing access to a small amount of information and requiring little to no user input, Web 1.0, also known as the Static Web, was the earliest and most secure internet in the 1990s.
Making user pages or simply commenting on articles wasn’t common back then.
Users found it very challenging to locate relevant data in Web 1.0 because there were no algorithms for sorting internet pages.
Simply described, it was a one-way street with a little pathway where a few created the material and the majority of the information came from directories.
Web 2.0 (2005-present)
Thanks to developments in online technologies like Javascript, HTML5, CSS3, etc., the Social Web, or Web 2.0, makes the internet much more interactive.
This made it possible for start-ups to create dynamic web platforms like YouTube, Facebook, Wikipedia, and many more.
Since data can now be transferred and shared between different platforms and applications, this prepared the way for social networks and the creation of user-generated content to grow.
Many web founders, including the famous Jeffrey Zeldman, contributed to the development of the tools used in this period of the internet.
Web 3.0 (yet to come)
The next stage of the web’s development, known as Web 3.0, aims to give the internet a near-human level of intelligence by using AI systems to run smart applications that can help users.
The Semantic Web is intended to “automatically” interface with systems, people, and domestic appliances, according to Tim Berners-Lee.
As a result, both humans and machines will be involved in the content development and decision-making processes.
This would make it possible to intelligently produce and provide highly-tailored content to every internet user.
Features of Web 3.0
The design of Web 3.0 may take into account accessible characteristics, semantic web, and AI.
The reason for employing AI is to give people faster access to more accurate data.
An AI-powered website should be able to sort through the data and present the information it believes a particular user will find useful.
Since the results are websites that users have voted on, social bookmarking as a search engine can produce better results than Google.
These results, however, are equally subject to human control. AI might be used to distinguish between genuine and fake results, providing outcomes similar to social media marketing and social bookmarking but without negative feedback.
The following are a few critical factors of Web 3.0 that help define what the third generation of the web is expected to be all about:
- Ubiquity
- Semantic Web
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Graphics
- Decentralized
- Blockchain
- Cryptocurrency
- Autonomous and Artificially intelligent
Applications of Web 3.0

The capacity to absorb massive amounts of information and transform it into factual knowledge and practical applications for users is a frequent requirement for a Web 3.0 application.
The fact that these applications are still in the early phases means that they have a lot of opportunity for improvement and are very different from the potential functionality of Web 3.0 apps.
Amazon, Apple, and Google are a few of the businesses that are creating or existing products that they are changing into Internet 3.0 apps.
Web 3.0 Examples
- Siri
- Wolfram Alpha
- NFT
- Cryptocurrency
- dApp
- Cross-chain bridges
- DAOs
Conclusion
The new internet will offer a more personalized and tailored surfing experience, a more knowledgeable and human-like search helper, and other decentralized advantages that are believed to contribute to the creation of a more equal web.
This will be accomplished by giving each user freedom over their data and improving the overall user experience as a result of the numerous improvements that will be implemented once it is in place.
FAQs
Web 3.0 Crypto: What is it?
Which Web3 crypto is best?
- Filecoin.
- Flux.
- Theta.
- The Graph.
- BitTorrent.
- Siacoin.
- Basic Attention Token.
- Polkadot.
Why would someone utilize Web3?
What is a Web3 example?
A peer-to-peer payment service that uses a blockchain might be an illustration of a Web3 application.
People could pay for a good or service using a decentralized app (Dapp) designed for payments rather than a bank.

